
Collection of Phytopathogenic and Agriculturally Beneficial Bacteria (VURV–B)
Collection of phytopathogenic and agriculturally beneficial bacteria (CPABB) is one of the founding collections of The Czech National Programme on Conservation and Utilization of Microbial Genetic Resources Important for Agriculture. The collection currently includes:
1) Strains of quarantine bacterial plant pathogens and other plant pathogenic bacteria causing severe extensive damage to field and greenhouse crops, to forests, orchards and ornamental plants.
2) Strains of agriculturally beneficial bacteria supporting growth and viability of plants and concomitant bacteria which demonstrate properties of biotechnological values for agricultural research and practice.
Collection of phytopathogenic and agriculturally beneficial bacteria is administrated and maintained by staffs of team of Phytobacteriology, the only workplace in the Czech Republic specializing in bacterial plant diseases. Our laboratory, greenhouse and experimental plots in Slaný have a working permit to handle group 2 microorganisms.
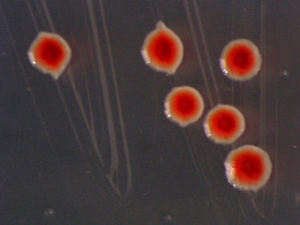
The Plant-Pathogenic Bacteria Database includes 270 strains of 19 genera and 44 species: https://www.vurv.cz/collections/vurv.exe/list?lang=cz&org=BA&term=&coll={9ABB1809-129E-4165-AF01-60B5EB319A25}&cond=AND&rows=20&item_no=1
Agrobacterium, Bacillus, Clavibacter, Curtobacterium, Dickeya, Erwinia, Flavobacterium, Leifsonia, Microbacterium, Mycobacterium, Paenibacillus, Pantoea, Pectobacterium, Pseudomonas, Ralstonia, Rhizobium, Stenotrophomonas, Streptomyces, Xanthomonas
• Activities
Monitoring of causal agents of bacterial diseases and other accompanying bacteria important for the agricultural crops production and food processing industry, orchards, ornamental horticulture and forests in the Czech Republic.
Epidemiology and genetic variability of plant pathogenic bacteria.
Determination of characteristic features of individual strains of bacteria - microscopic, biochemical, genetic and chemical, virulence and pathogenicity and another specific properties - surface tension, ice nucleation activity, antagonistic properties, resistance to antimicrobial chemical agents.
Deposition and maintaining of plant pathogenic bacterial strains.
Online providing evidence of the deposited strains of bacteria and tables summarizing their characteristics.
• Services
Providing deposited bacterial strains with guaranteed characteristics in the required quality and quantity.
Reference strains for diagnostic laboratories.
Rapid identification services based on automated fatty acid profilig - FAME, characterisation methods - including nutritional profilig - Biolog, genetic profilig – real-time PCR, HRM.
Expert activities - diagnostics of causal agent of bacterial diseases of plants and bacterial contaminants in the processing of agricultural crops in food technology.
Training and educational activities - for civil servants, agricultural companies, diagnostic laboratories, high schools, universities, students and professionals.
Teaching – lectures for middle and high schools, assistance in the preparation of thesis or dissertation.
International exchange - research centres, universities.
Depositing of new strains important for agricultural as well as basic and applied researches after the acceptance process.
• Preservation
Most of the bacterial strains are cryopreserved at - 90°C.
Major part of deposited strains is freeze dried and stored at room temperature.
All cultures delivered by CPPB are for immediate use – particularly as actively growing cultures on nutrient agar plates or slants.
DNAs are stored in TE buffer at -30°C and are sent particularly at room temperature.
All strains are checked after preservation for viability, purity, virulence and pathogenicity after intervals scheduled for the different taxa.
Bacterial strains provided for deposit are tested by subculturing at least once a year.
Application:
• Contact and information for customers
All strains are supplied within 2-4 weeks according type and number of strains.
Terms and conditions form will be send to customer before expedition.
The only cost would be the shipping charges.
Customer agrees to cite the CPPB strain number(s) in publications and applications and is kindly requested to provide the CPPB with details of the related publications.
Contact:
Czech Agrifood Research Center
Team of Phytobacteriology
Drnovská 507
161 06 Praha 6 – Ruzyně
Czech Republic
https://www.carc.cz
Staff:
Ing. Iveta Pánková, Ph.D. - pankovai@vurv.cz, 702 087 647, 233 022 289 (responsible person)
Ing. Václav Krejzar, Ph.D. - krejzar@vurv.cz, 702 087 648, 233 022 470
Ing. Radka Krejzarová, Ph.D., Ing. Barbora Soukupová
|
|






















 Closing the vials before lyophilization
Closing the vials before lyophilization Lyophilizer Cryodos 50
Lyophilizer Cryodos 50 Storage of lyophilized cultures
Storage of lyophilized cultures Microscope Olympus BX-43
Microscope Olympus BX-43 Microscopic control of cultures
Microscopic control of cultures Thermal cycler Biometra
Thermal cycler Biometra Biohazard flow box
Biohazard flow box Cryopreservation in the freezer
Cryopreservation in the freezer Cultures in broths and in lyophilized form
Cultures in broths and in lyophilized form









 Collection of Brewery Microorganisms (RIBM), (VÚPS, a. s., Praha)
Collection of Brewery Microorganisms (RIBM), (VÚPS, a. s., Praha) Collection of Animal Pathogenic Microorganisms (CAPM),
Collection of Animal Pathogenic Microorganisms (CAPM),

 Czech Collection of Microorganisms (CCM), (MU, Brno)
Czech Collection of Microorganisms (CCM), (MU, Brno)